"Viuda Negra" Convertida en Pulsar
Researchers have used raw computing power to hunt down a 'black widow' pulsar that is evaporating its companion star.
Pulsars
are stellar remnants that emit lighthouse-like beams of radiation. They
often emit gamma rays, but can usually be spotted only if they also
emit easier-to-detect radio waves. However, Holger Pletsch of the Max
Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Hannover, Germany, and his
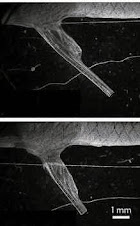
colleagues found the current pulsar (pictured; circled) through a blind
search of data from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope.
Using
computers to analyse huge swathes of raw data, the team picked out the
pulsar, which takes 93 minutes to orbit its companion star. This orbital
period is the shortest of any binary pulsar of this type yet found.
- Nature: 491, 10 (01 November 2012)